Research Highlights
Seok-Yong Choi’s lab is performing research on the topics listed below using zebrafish as a model organism. Taking advantage of its easiness in carrying out drug screen, we are developing drugs related to respective research topic collaborating with Professor Jin Hee Ahn in Department of Chemistry at Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST).
"Please click the respective images below to enlarge"
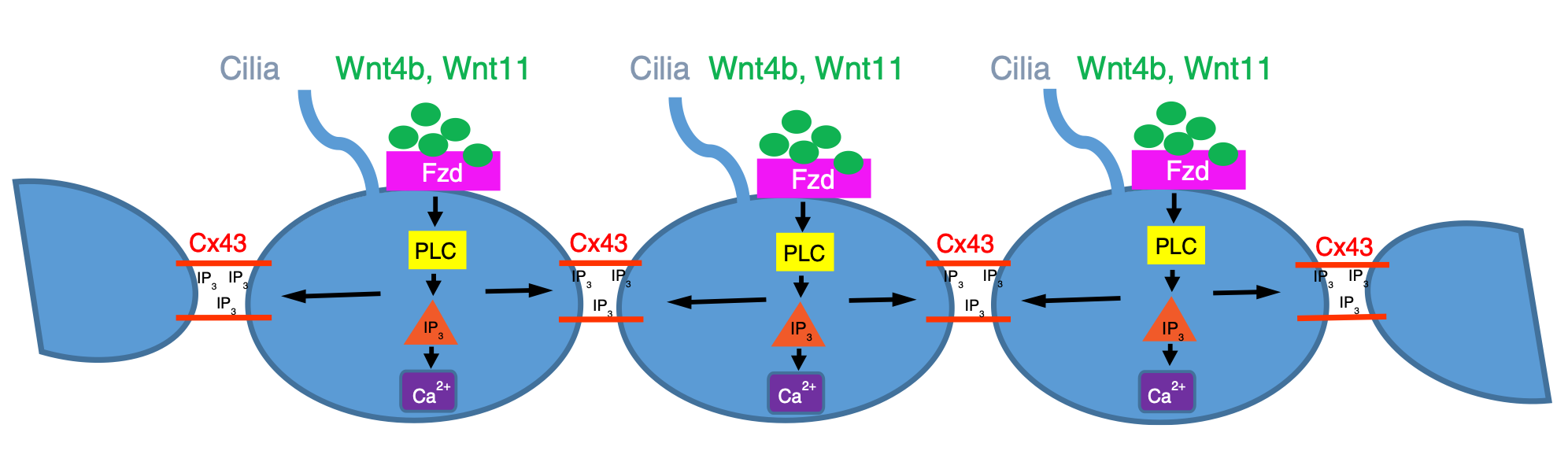
Molecular mechanism of regeneration of motile cilia
Motile cilia exist in ependymal cells in brain ventricles and spinal central canal, oviduct epithelial cells and respiratory epithelial cells, and are involved in flow of cerebrospinal fluid, migration of oocytes and removal of mucus, respectively. As such, defect in motile cilia leads to hydrocephalus, infertility and respiratory infection.
We are investigating the molecular mechanism underlying restoration of defective motile cilia and thus developing small molecules that regenerate motile cilia.
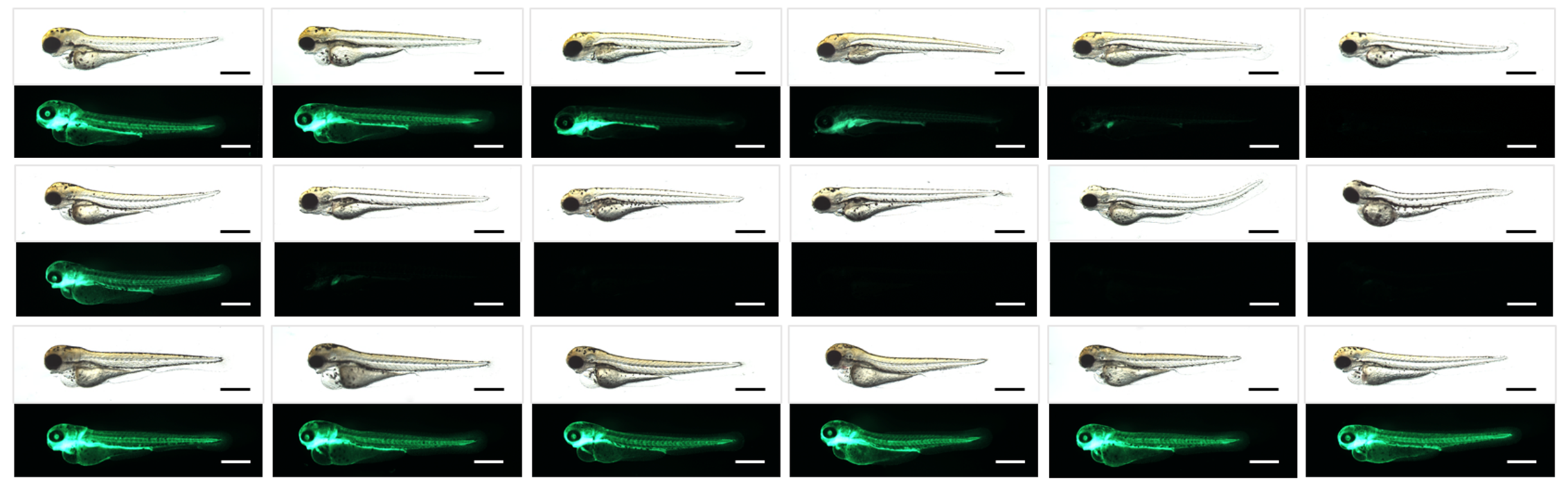
Development of Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) antagonists
AhR was previously known as receptor of xenobiotics such as dioxin, yet its research is very active worldwide because it has been reported to be implicated in stem cell biology, immunity and infection.
Using transgenic AhR reporter zebrafish and small molecule library, we have identified AhR antagonists. We are currently improving their efficacy by optimizing lead compounds.
We recently found that AhR antagonist we developed exhibited anti-viral activity against SARS-CoV-2, virus causing COVID-19.
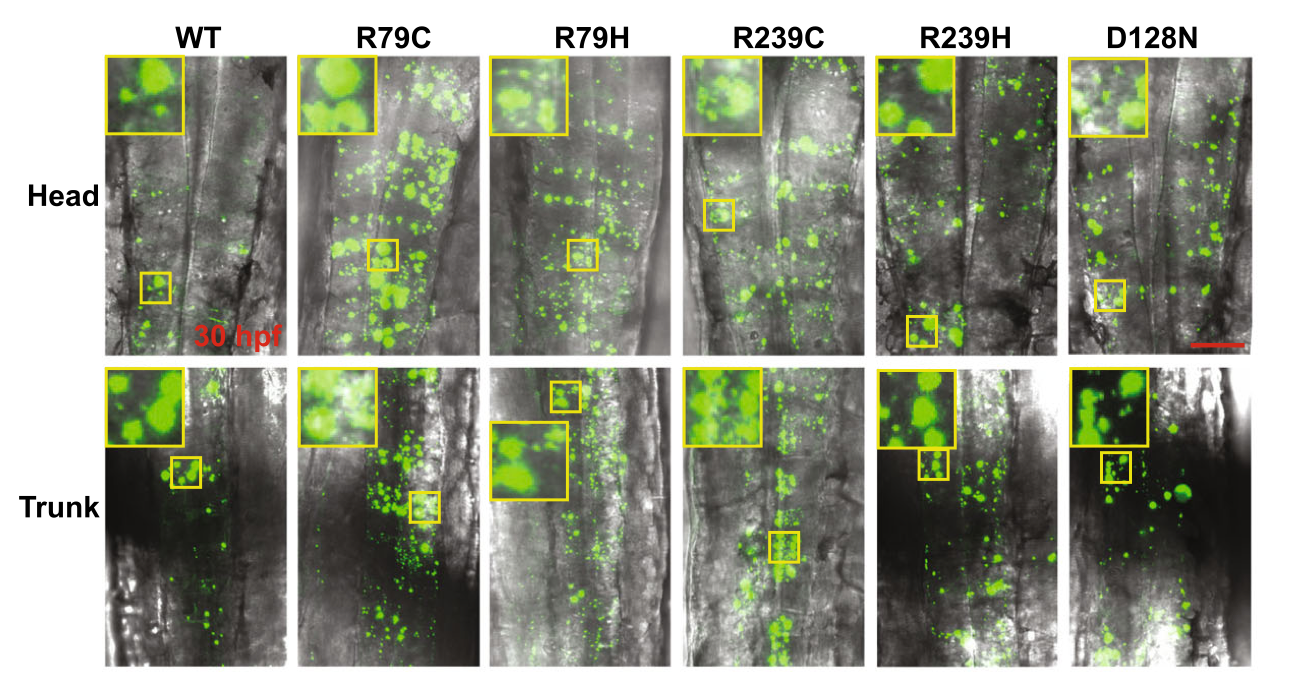
Molecular diagnosis of human genetic diseases
Advent of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) dramatically reduced time and expense required for sequencing of human genome, which makes it much easier to identify causative gene of human genetic diseases. However, functional study including research on animal model is critical to prove the causality.
We are identifying causative genes responsible for human neurological genetic diseases and determining how mutations of these genes elicit the diseases, collaborating with Professors Myeong-Kyu Kim and Tai-Seung Nam in Department of Neurology at Chonnam National University Medical School.
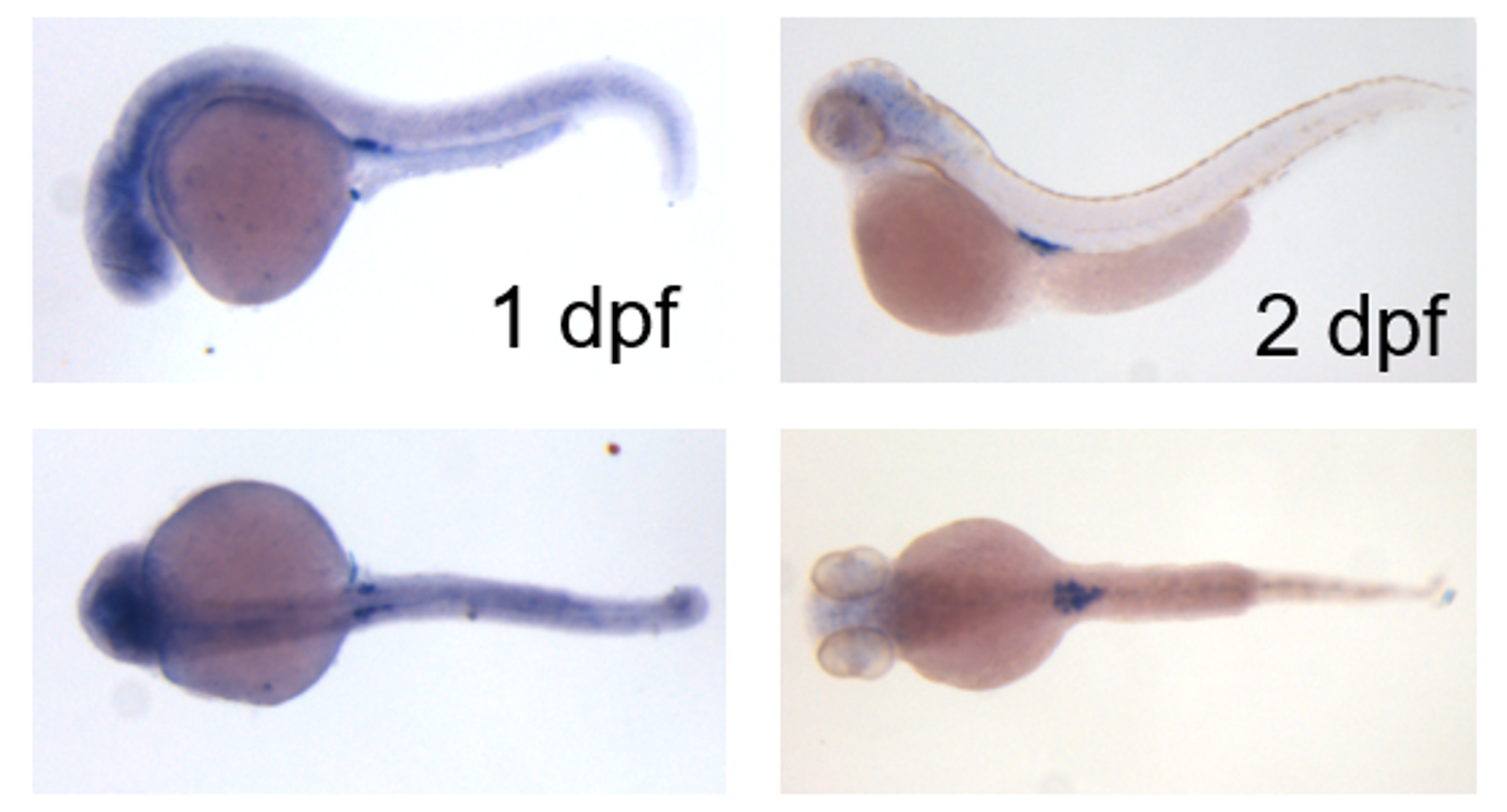
Molecular mechanism of sex determination in zebrafish
Sex is determined by either sex chromosomes or environmental factors such as tempature and density. However, neither sex chromosomes nor environmental factors have been known to be involved in sex determination to date.
We recently found that lack of mitoPLD, a key player in mitochondrial fusion and piRNA generation, leads to gonadless zebrafish with male appearance, and are currently studying how mitoPLD regulates SD in zebrafish.



